In this section
Introduction:
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, which is the most widely used language on Web to develop web pages. HTML was created by Berners-Lee in late 1991 but "HTML 2.0" was the first standard HTML specification which was published in 1995. HTML 4.01 was a major version of HTML and it was published in late 1999. Though HTML 4.01 version is widely used but currently we are having HTML-5 version which is an extension to HTML 4.01, and this version was published in 2012.
- HTML is not a programming language. It is a markup language that tells browser how to structure web pages.
- It Consists of series of elements which we use to enclose, wrap or markup different parts of the contents to make it appear or act in certain way.
- HTML 5 is the latest evolution of the standard that defines HTML.
- HTML 5 define two different concepts:
- It is a new version of the language with new elements and attributes.
- A larger set of technologies that allows building more diverse and powerful website and application.
Important features of HTML 5:
- Semantics: Allowing us to describe more precisely what our content is.
- Multimedia: Incorporation of special element for audio and video embedding.
- Device Access: Allowing for usage of various input and output devices.
- Performance and Integration: Providing greater speed optimization and better usage of computer hardware.
Basic Building Block
- Opening Tag: This consists of name of the element. It marks where the element begins.
- Content: Information of the element.
- Closing Tag: This marks end of the element and it precedes tag name with a forward slash.
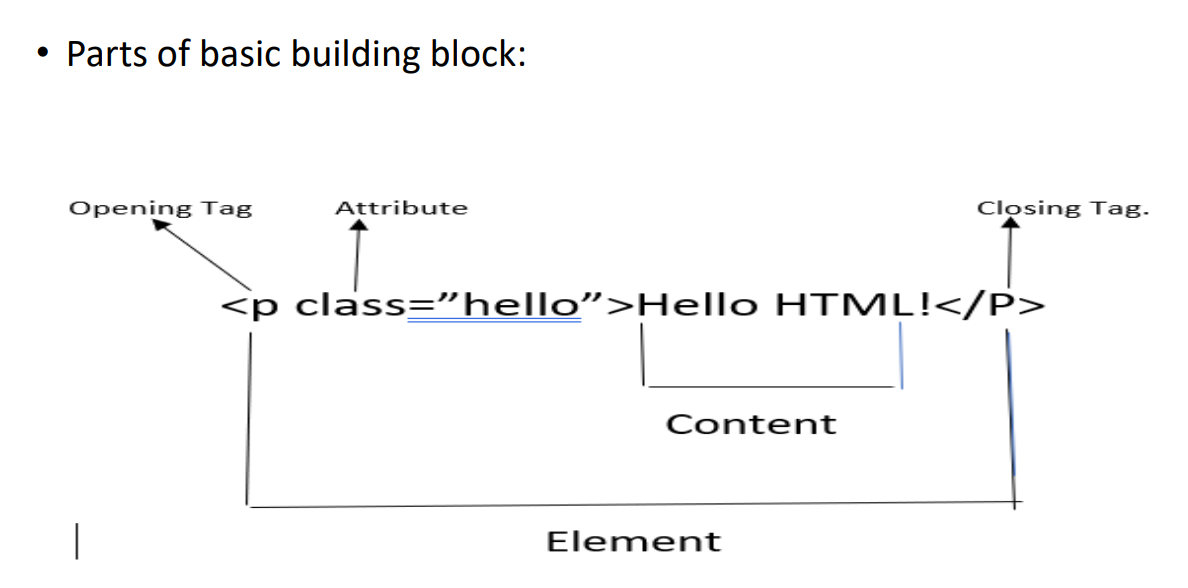
• So, an element in HTML is: Opening tag, followed by content, followed by closing tag.
• Note-1: Content “Hello HTML!”, has a semantics/meaning now. What is it?
• Note-2: HTML is not case in-sensitive.
Basic structure of HTML file
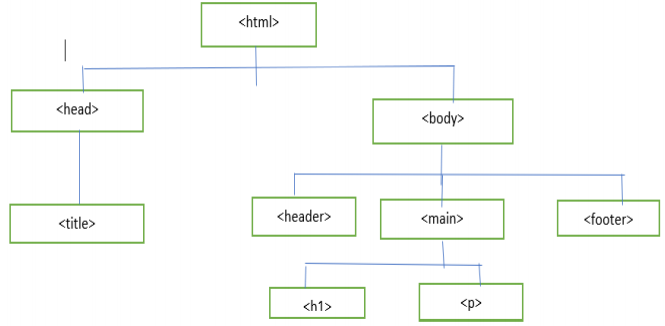
Elements, Attribute and Tag
HTML uses predefined tags and elements which tells the browser about content
display
property.
If a tag is not closed then browser applies that effect till end of page.
- Block-level Element:
- These elements are the structural element of HTML.
- These forms the visible parts of the page. A block-level element appear in new line following the content that precedes it.
- Ex.: Heading, Paragraph, Lists, Navigation, Footer and so on.
- Block-level elements can be nested within another block-level element but not within a inline-element.
- Inline Element:
- Inline Element are contained within block-level element and surrounds only small parts of the document.
- No new line after inline element in the document.
- Ex. Include: <a>, <em>, <strong> and many more.
- Empty Element:
- Not all elements follow the patterns of opening tag, content and closing tag. Some elements only consists of single element, such element are called empty element.
- Ex. <img src=“imag.jpeg”>
- Attribute:
- Attribute contain extra information about the element that won’t appear in the content.
- In this ex. Class attribute is an identifying name used to target the element with style or JavaScript information.
- Boolean Attribute:
- Attribute written without values. They can have only one value, which is generally the same as the attribute-name.
- Ex. <input type=“text” disabled = “disabled”>
- Ex. <input type=“text” disable< [Note: Using disabled attribute prevents the end-user from entering text into the input box.]
- White Space in HTML:
- HTML parser reduce each sequence of white space to a single space, when rendering the code.
- However, proper space allows better readability of the code.
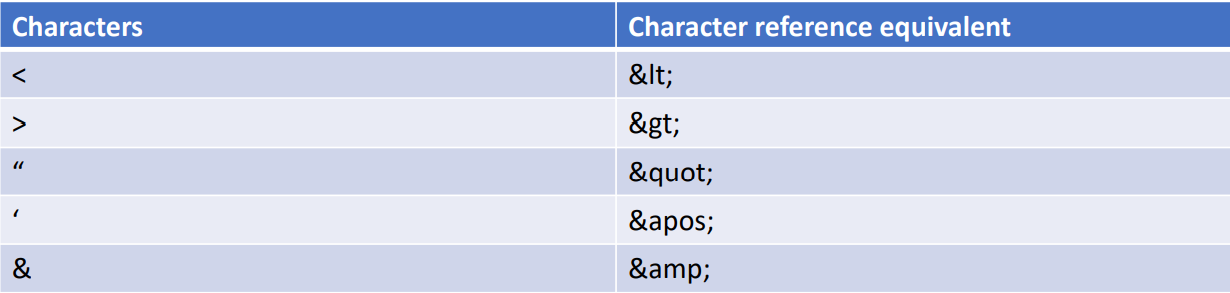
- Entity Reference:
- Characters < ,>,”,’ and & are special character. They are parts of the HTML syntax.
- Special codes called character reference/entity reference are used to render special character.
- Each reference starts with a ampersand(&) and ends with a semicolon(;).
- HTML Comments:
- The purpose of comments is to allow us to include notes in the code to explain our logic.
- Browser ignores comments. Syntax : <!-- -->
- Paragraph and Heading element: <p></p>, <h1><h2></h2>..<h6></h6>…</h2></h1>.
- Paragraphs are wrapped using <p></p> tag.
- <h1> represents main heading, <h2> represents sub-heading, <h3> represents sub-sub-heading and so on.
- List Element:
- Un-ordered list: Un-ordered list are used to mark up lists of items for which the order of the item doesn’t matter.
- Book.
- Pen.
- Ordered list: In ordered list, order of the item does matter.
- Go straight.
- Turn Left.
- Description List:
- The propose of this list is to markup a set of item and their associated descriptions, such as terms and definitions.
- It uses <dl> as a wrapper and in addition uses <dt> (description term) element, and each description is wrapped in a <dd> (description definition) element.
- Computer Science.
- Evolving.
- Single term can have multiple description.
Ex.
<ul>
<li> Book </li>
<li> Pen </li>
</ul>
Output:
Ex.
<ol>
<li> Go straight.</li>
<li> Turn Left. </li>
</ol>
Ex.
<dl>
<dt> Computer Science. </dt>
<dd> Evolving. </dd>
</dl>
- <code>
- <pre>
- <var>
- <samp>
- <header>
- <nav>
- <main>
- <aside>
- <footer>
- <span>
- <div>